Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits)
What is Phishing?
Definition and meaning of Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits)
Phishing is a protection Make the most in which a offender imPersonates a legitimate commercial enterprise or authentic Character in order to accumulate Private and sensitive Data inclusive of credit score card numbers, personal idEntity numbers (PINs), and Passwords.
Phishing relies on technical deception, as well as Social Engineering techniques designed to control the victim into taking precise action on behalf of the Attacker, which includes clicking on a malicious link, Downloading and/or commencing a malicious e-mail attachment, or divulging facts the attacker can use in a future assault.
According to a Joint mission run by way of the USA Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), 90% of all Cyberattacks start with phishing. One of the key motives at the back of the superiority of phishing assaults is the Attack Vector’s versatility and excessive go back on funding for Cybercriminals.
To mitigate the dangers related to phishing, individuals and groups want to prioritize phishing cognizance education, put into effect roBust Email Filtering, take into account the usage of anti-phishing Cloud offerings, and comply with Best Practices for secure Online behavior.
How Phishing Works: Phishing Attack Indicators
In a successful phishing strive, one of the scammer’s primary Objective is to gain the victim’s agree with. To achieve this, scammers use each technical and mental tactics to make verbal excHange with ability victims seem credible and legitimate.
To safeguard in opposition to phishing scams, it’s important for people to understand the indicators of a phishing assault in e mail, voice, and textual content messages. It’s critical to be wary of messages that ask for private statistics inclusive of login Credentials, credit score card numbers, or Social Security numbers. One of the biggest telltale symptoms is that the communication is unsolicited and it requests touchy data or asks the victim to verify touchy data. Legitimate corporations commonly do now not make such requests thru Electronic Mail, textual content or voice messages.
If the sender’s touch Records doesn’t exactly suit what might be predicted from the valid source, that’s some other Signal the unsolicited communique can also be a phishing strive. Phishers frequently use deceptive e-mail addresses that carefully resemble a valid entities and contact numbers that don’t fit the valid entity’s viciNity Code.
Some phishers, but, use compromised legitimate e mail money owed or telephone numbers to conduct their attacks. This could make it tougher to identify discrepancies in contact inFormation.
That’s why other factors, consisting of the message content material, look and standard Context of the request, should additionally be taken under consideration whilst evaLuating the authenticity of a verbal exchange. Any unsolicited communique that requests sensitive facts to be validated have to be seemed as a probable phishing strive.
Types and Examples of Phishing Exploits
Phishing exploits may be adapted to fulfill the desires of various sorts of objectives and assault objectives. It’s this versatility that permits cybercriminals to select the communication medium that fits their target audience and targets and solid either a large Internet designed to boom the danger of locating a vulnerable target – or a narrow internet designed to catch a specific victim.
Popular varieties of phishing exploits include:
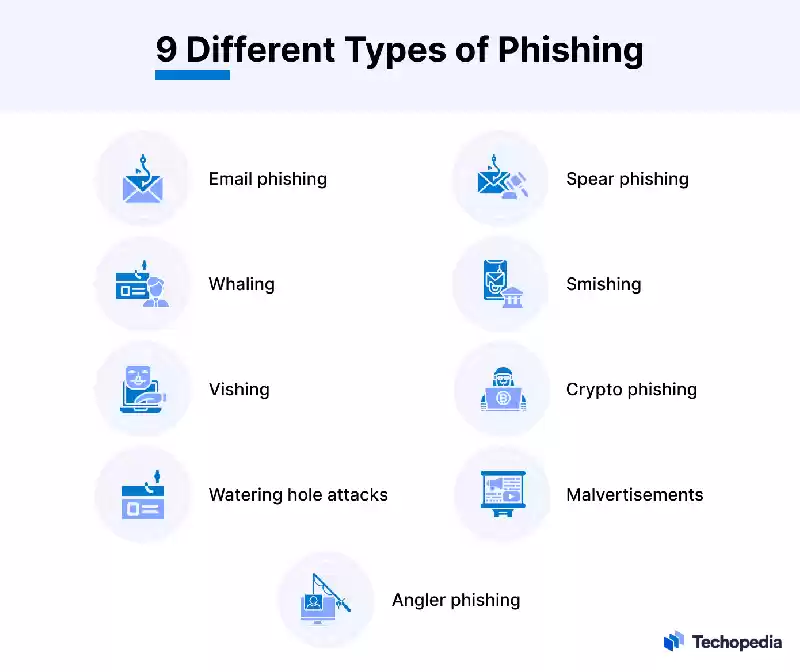
Email Phishing
This is the most not unusual sort of phishing assault. The attacker sends an email that appears to be from a valid supply, which include a bank, credit score card business enterprise, or government organisation. The e-mail regularly consists of a link that, when clicked, takes the sufferer to a fake internet site that seems like the real internet site. Once the victim enters their login credentials or different sensitive records on the faux internet site, the scammers can steal it.
Chatbots that use Generative AI have made it simpler than ever for phishers to craft e mail communications that seem like from a legitimate source.
Here are some examples of e mail phishing scams:
- Invoice rip-off: The scammer sends an electronic mail that looks to be from a valid employer, inclusive of a application corporation or credit score card company. The e mail says that the victim has an unpaid invoice and asks them to click on a Hyperlink to pay it. The link takes the victim to a faux Website that looks like a actual internet site. Once the victim enters their payment facts at the fake website, the scammers can thieve it.
- Password reset rip-off: The scammer sends an e mail that appears to be from a valid company, which include a bank or Social Media website. The electronic mail says that the victim’s password has been reset and asks them to click on a hyperlink to exchange it. The hyperlink takes the victim to a fake website that seems like a real website. Once the victim enters their new password at the faux internet site, the scammers can steal it.
- Tech aid scam: The scammer sends an email that looks to be from a legitimate tech guide business enterprise. The e-mail says that the victim’s pc has a problem and asks them to call a sure wide Variety for help. When the sufferer calls the variety, they're related to a scammer who will try and persuade them to give them far off get right of entry to to their pc. Once the scammer has remote get admission to to the victim’s Laptop, they could steal their personal statistics or deploy malware.

Spear Phishing
This is a Greater targeted sort of phishing attack wherein the attacker crafts a communique this is in particular tailor-made to the sufferer. For Instance, the attacker’s e mail might be approximately a subject that the sufferer has shown previous hobby in due to the fact it's miles applicable to their work. When Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine mastering (ML) are used for personalisation, the e-mail is much more likely to be opened, and the sufferer is much more likely to fall for the scam.
Here are some examples of spear phishing scams:
- Targeted e mail scam: The scammer sends an electronic mail that is specifically tailored to the victim. The email may additionally point out the victim’s call, organization, or different non-Public facts. Personalization makes the email more likely to be opened, and the victim is much more likely to fall for the rip-off.
- Business e-mail compromise (BEC) rip-off: The scammer sends an email that looks to be from a valid commercial enterprise accomplice, consisting of a dealer or Client. The electronic mail may also ask the victim to make a Charge or change their password. The scammer will often use a feel of urgency to stress the sufferer into acting quickly.
- Appeal to authority rip-off:The scammer sends an e mail that appears to be from a excessive-degree executive whose name the victim is probable to recognise. The email asks the sufferer to twine cash to a specific account, typically foreign places. The scammer will often use a sense of urgency to stress the sufferer into appearing fast.
Whaling
This kind of spear phishing attack seeks to make the most a “very big fish,” which includes a big corporation’s Chief Financial Officer (CFO) or every other C-stage government.
Here are a few examples of whaling scams:
- CEO fraud: The scammer sends an e-mail to the Vice President of Finance that looks to be from the enterprise’s Chief Executive Officer. The e-mail urges the capability victim to right away take a specific movement on behalf of the scammer so as to ultimately result in monetary loss or the unauthorized launch of touchy data.
- Vendor impersonation rip-off: The scammer sends an electronic mail to the Vice President of Procurement that appears to be from a person the victim’s corporation does commercial enterprise with. The bogus e-mail asks the sufferer to authorize charge for an invoice that is allegedly “past due” or exchange a shipPing deal with for a large order.
- Internal worker rip-off: The scammer goals the Vice President of Sales and sends an electronic mail designed to trick them into taking a selected motion as a way to supply the attacker get entry to to touchy records in customer information.
Smishing
This form of phishing take advantage of uses SMS text messages to speak with the target. The textual content messages will often comprise a hyperlink that, when clicked, takes the sufferer to a faux website or asks the victim to provide touchy facts.
Here are some examples of smishing scams:
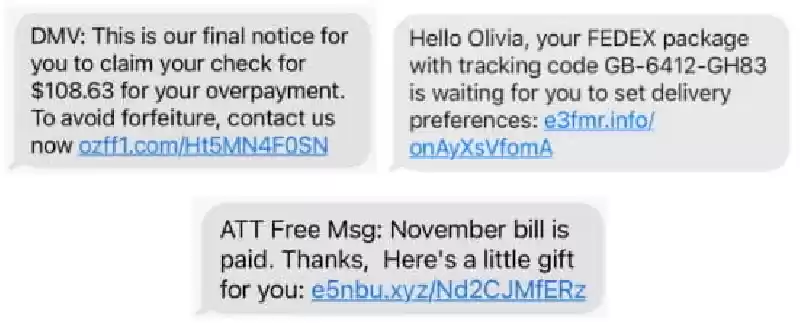
- Parcel transport rip-off: The scammer sends a textual content message that appears to be from a transport company, including UPS or FedEx. The message says that the sufferer has a Package expecting them and asks them to click on a hyperlink to track it. The hyperlink takes the victim to a fake website that looks like a actual shipping company website. Once the victim enters their private records on the fake internet site, the scammers can steal it.
- Banking rip-off: The scammer sends a textual content message that looks to be from a financial institution, including Bank of America or Wells Fargo. The message says that the victim’s account has been compromised and asks them to click on on a hyperlink to verify their facts. The link takes the sufferer to a faux website that looks like the real bank internet site. Once the sufferer enters their login credentials at the faux internet site, the scammers can scouse borrow them.
- Password reset rip-off: The scammer sends a text message that looks to be from a popular organisation which includes Amazon or eBay. The message says that the victim’s password has been compromised and asks them to click on on a link to trade it. The hyperlink takes the victim to a fake internet site that seems like a actual internet site. Once the victim enters their antique password a good way to exchange it to a new password on the faux internet site, the scammers can steal it.
Vishing
This type of phishing take advantage of is performed by way of telephone. The attacker makes use of their very own voice, or an AI-generated voice, to impersonate a representative from a legitimate employer or company.
Here are some examples of vishing scams:
- Tech aid scam: The scammer calls the sufferer and claims to be from a valid tech aid agency. They inform the sufferer that their laptop has a hassle and ask for permission to get right of entry to the laptop remotely. Once the scammer has been granted far off get admission to to the victim’s pc, they can scouse borrow their private statistics or deploy malware.
- Government impersonation rip-off: The scammer calls the victim and claims to be from a government company, which include the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or Social Security Administration. They will inform the victim that they owe money and ask them to pay it over the Cellphone. In this sort of phishing make the most, the scammer might also use threats or intimidation to pressure the sufferer into paying.
- Sweepstakes rip-off: The scammer calls the sufferer and informs them that they've gained a prize in a sweepstakes or lottery. They will ask the victim to offer personal facts, including their social safety wide variety or financial institution account Range, which will claim the prize. The scammer will then use the victim’s records to scouse borrow cash or behavior Identity Theft.
Crypto Phishing
This form of scam targets Cryptocurrency traders and traders. The scammers ship emails or messages that seem like from a legitimate supply, along with a cryptocurrency alternate or wallet company. The emails or messages often include a hyperlink that, while clicked, takes the victim to a faux internet site that seems like the actual website. When the sufferer enters their login credentials or different sensitive records at the faux website, the scammers can scouse borrow the information.
Here are a few examples of crypto phishing scams:
- Security caution rip-off: The scammer sends an e mail that looks to be from a Cryptocurrency Exchange, caution the sufferer that their account has been compromised. The email asks the sufferer to click on on a hyperlink to confirm their account. The hyperlink takes the sufferer to a faux internet site that looks like the actual change website. Once the sufferer enters their login credentials on the fake internet site, the scammers can thieve them.
- Giveaway scam: The scammer sends a message on social Media that looks to be from a celebrity or Influencer. The message asks the sufferer to ship cryptocurrency to a certain deal with to enter a contest or crypto giveaway. The deal with belongs to the scammer, and the victim’s cryptocurrency can be stolen.
- Counterfeit internet site rip-off: The scammer creates a fake cryptocurrency internet site that looks as if a legitimate trade or pockets issuer. The scammer then advertises the fake website on social media or other online sySTEMs. When victims go to the fake website and input their login credentials, the scammers can thieve them.
Watering Hole Attacks
This sort of phishing rip-off goals websites that professionals inside a selected industry or market section are in all likelihood to visit.
Here are a few examples of watering hole scams:
- CommUnity discussion board rip-off: The scammer compromises an industry-unique discussion board or Network internet site that professionals in a selected Field are likely to visit. When centered individuals go to the forum, their Devices are inFlamed with malware, or they are directed to a fake login Web Page a good way to harvest their credentials.
- Employee portal scam: The scammer targets an worker benefits portal or Intranet web site that personnel often get admission to to manipulate their advantages, View pay Stubs, or get entry to agency sources. By compromising this portal, the attacker can probably steal employees’ login credentials and personal facts or maybe inject malware into their gadgets. This facts may be used for company espionage or in addition attacks in the organization’s community.
- Malicious VPN scam: The attacker creates a fake internet site that gives Access to unfastened VPNs. People who sign on to apply the factitious virtual personal networks are susceptible to having their credit card information stolen, personal photos and videos leaked or sold on-line, and private conversations recorded and sent to the attacker’s Server.
Malvertisements
This sort of phishing attack places malicious ads on legitimate websites. When sufferers click on on the commercials, they are taken to a faux website on the way to infect them with malware.
Here are some examples of Malvertising scams:
- Drive-via down load rip-off: This form of scam occurs whilst malware is routinely Mounted on a user’s laptop after they go to a website that has been inflamed with Malicious Code. The malware may be used to thieve personal facts, set up other malware, or take control of the pc.
- Pop-Up Ad scam: This sort of rip-off entails displaying undesirable pop-up commercials on a user’s laptop. The commercials might also incorporate malicious code to hiJack the sufferer’s browser or allow the attacker to transport laterally thru the sufferer’s network and search for other vulnerabilities to make the most.
- Clickjacking scam: This sort of scam entails tricking a consumer into clicking on a malicious hyperlink or internet site button. The hyperlink or button might also look like legitimate, but it is in reality designed to install malware or scouse borrow non-public data.
Angler Phishing
This kind of phishing assault makes use of famous social media web sites like Facebook and TikTok because the attack Vector. The attacker creates fake social media bills to engage with real users on social media systems and benefit their agree with. Eventually, the attacker will send a right away message (DM) or put up something on the website that incorporates a hyperlink to a phishing internet site.
Examples of angler scams encompass:
- Complaints on social media: In this rip-off, the attacker creates a fake social media account that looks as if a legitimate customer service account for a organization. They then attain out to people who have published complaints about the organisation on social media and provide to “assist” them solve their issues. The attacker will then redirect the sufferer to a phishing website that asks for the victim’s electronic mail cope with, phone variety, or other personal statistics the attacker can use to steal the sufferer’s identification.
- Community web page scams: In this rip-off, the attacker creates a fake network page that requires personal facts such as a name, address, or cellphone variety earlier than get admission to will be granted. Once the scammer has accumulated the victim’s data, they could use it with different statistics to dedicate fraud or identification theft.
- Refund scams: In this rip-off, the attacker sends an email or textual content message that looks to be from a valid enterprise, which include a financial institution or credit score card organization. The e-mail or text message will say that the sufferer is owed a reimbursement and presents the sufferer with a hyperlink to claim it. The hyperlink will take the sufferer to a faux internet site that seems like the legitimate company’s internet site. Once the sufferer enters their personal records on the faux website, the attacker can thieve it.
Psychological Strategies Used in Phishing
Phishing techniques for buying a sufferer to carry out a particular movement on behalf of the attacker frequently take advantage of human psychology. By masquerading as trusted entities, developing a feel of urgency, or attractive to victims’ preference to assist or be a part of a set, an attacker can spark off impulsive responses.
While technical Methods consisting of e-mail Spoofing, Domain mimicry, or malware transport are important additives, it’s the psychological manipulation that frequently determines achievement. Ironically, most of the techniques that phishers use are well-known Advertising and marketing techniques.
Psychological strategies used to perform a hit assaults encompass:
- Creating a Sense of Urgency: Phishers often layout their communique to have a sense of urgency. People have a tendency to prioritize pressing matters and are much more likely to behave impulsively when they understand a time-touchy threat.
- Inspiring Fear: The attacker’s verbal exchange will claim the sufferer’s account could be suspended, or criminal action could be taken except they act without delay. Fearful people are much more likely to react impulsively.
- Inspiring CuriOSity: The attacker’s verbal exchange is designed to pique the victim’s interest with the aid of offering incorrect statistics or tantalizing info in order to spark off them to click on on a hyperlink or open an attachment to research greater.
- Appealing to Authority: The phisher’s communique appears to be from an authority determine like a CEO, IT administrator, or authorities reliable.
- Appealing to Familiarity: The attacker uses the victim’s accept as true with in a recognized emblem, agency, or person to create a fake sense of protection.
- Creating a Sense of Scarcity: The attacker creates the perception of exclusivity or restricted Availability to inspire sufferers to do so fast.
- Inspiring Guilt: The attacker’s conversation is designed to make the victim experience guilty or ashamed for now not complying with a request by using claiming the communication is not the primary one sent.
- Using Social Proofs: The attacker affords fake testimonials, endorsements, or references to make the request seem honest and socially established.
- Encouraging Reciprocity: The attacker offers something of perceived value to the victim (along with a Discount or Freebie) in alternate for his or her taking a desired action.
- Appealing to the Past: The attacker’s conversation incorporates a request this is steady with a prior movement the sufferer is acquainted with.
- Appealing to Friendship: The attacker’s communique intently mimics the writing fashion of a colleague or friend so that you can lower the victim’s guard.
- Inspiring Sympathy: The attacker’s communique is designed to faucet into the victim’s feel of sympathy and preference to help the attacker out of a jam.
- Using FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): The attacker’s verbal exchange exploits the victim’s worry of missing out on an opportunity or occasion. Typically, the scammer will declare that instantaneous movement is required to participate.
- Appealing to Ingroup Biases: The attacker’s verbal exchange is designed to inspire a experience of belonging to a social group or “ingroup” the victim is familiar with. The phisher will craft phishing emails or messages that appear to come from assets that proportion a not unusual identity or characteristic with the goal.
Technical Techniques Used in Phishing
The psychological techniques above, while combined with the technical strategies below, are what make phishing assaults so extraordinarily powerful. When recipients act on mental triggers, they often fall victim to the technical traps hid within phishing emails, vishing telephone calls, and SMS text messages. (Editor’s Note: Attackers who lack the technical skills necessary to carry out an attack can purchase Phishing Kits on the dark internet.)
Technical strategies usually used in phishing attacks consist of:
Email Spoofing: The attacker manipulates email Headers so that they seem like from a relied on supply. Email spoofing is facilitated by way of weaknesses inside the standard Protocol for sending emails, Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). SMTP does now not require email senders to affirm the accuracy of the “From” address they offer, which makes it fairly clean for attackers to forge this information.
Link Manipulation: The attacker uses bogus hyperlinks in emails to direct sufferers to malicious web sites. Attackers regularly embed bogus URLs with valid Subdomains to bypass URL Filters.
Domain Spoofing: The attacker purchases domains that appear to be legitimate because they carefully resemble valid and famous domains.
Subdomain Takeover: The attacker identifies an enterprise’s inclined subdomains and takes control of them to Host phishing websites.
Attachment-Based Attacks: The attacker sends phishing emails with attachments that comprise Macros or Scripts that execute malicious code. The emails generally appoint social Engineering approaches designed to convince the recipient to enable the Macro Instructions or malicious scripts inside the attachment.
Malicious Redirects: The attacker makes use of hidden iFrames or JavaScript to redirect sufferers from legitimate websites to phishing pages.
Drive-By Downloads: The attacker exploits vulnerabilities in a victim’s browser or Software Program to down load and install malware without the victim’s understanding.
Obfuscation Techniques: The attacker employs Encoding or obfuscation strategies to hide malicious code within emails or web sites.
Dynamic Content Loading: The attacker uses an internet service or JavaScript framework, consisting of React or Angular, to create dynamic content that isn't always embedded in the website’s code. Dynamic content material generated on the fly can’t be detected detection with the aid of Static analysis.
JavaScript-Based Attacks: The attacker Inserts malicious JavaScript code in emails or on compromised web sites to deliver malware that enables a Ransomware assault.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: The attacker intercepts communication among the victim and a valid website to seize touchy facts.
Data Exfiltration: The attacker sends statistics stolen from victims’ gadgets to a server the attacker controls, so the data may be used afterward.
Credential Harvesting: The attacker creates faux login pages for famous services to Capture Usernames, passwords, and different credentials.
Session Hijacking: The attacker steals energetic consultation Cookies or Tokens to impersonate a user and benefit unauthorized get entry to to their money owed.
Tabnabbing: The attacker exploits the person’s trust in browser tabs by replacing inactive tabs with phishing pages.
Homograph Attacks: The attacker uses Unicode characters that look similar to Latin characters in Domain Names to lie to sufferers.
Content Spoofing: The attacker manipulates internet content on a compromised website to trick traffic into carrying out movements that benefit the attacker.
Email Forwarding: The attacker sets up e mail filters (policies) in compromised electronic mail bills as a way to mechanically ahead touchy messages that include account records to the attacker.
DNS Spoofing: The attacker manipulates DNS statistics to redirect users to faux web sites when they enter valid URLs.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): The attacker injects a malicious script into an internet web page’s code so that it will execute an action on behalf of the attacker. XSS may be used to scouse borrow consultation cookies, which can also include login credentials or different touchy data that allows the attacker to impersonate the sufferer.
Brand Impersonation: The attacker solicits touchy facts from the sufferer by using leveraging the consider they have got in a selected emblem call.
SQL Injection: The attacker enters in particular crafted SQL code into a website’s enter fields to benefit unauthorized get entry to to Databases the website makes use of. While SQL injection is greater commonly associated with records breaches and net utility attacks, it can be employed in phishing attacks to collect statistics or deliver malicious Payloads.
How to Prevent Phishing Attacks
With the touchy facts received from a a hit phishing rip-off, criminals can do harm to their sufferers’ financial histories, non-public reputations, and professional reputations that could take years to unravel. The combination of psychological and technical elements in phishing attacks amplifies their effectiveness and underscores the importance of cybersecurity education and robust defenses to counter those threats.
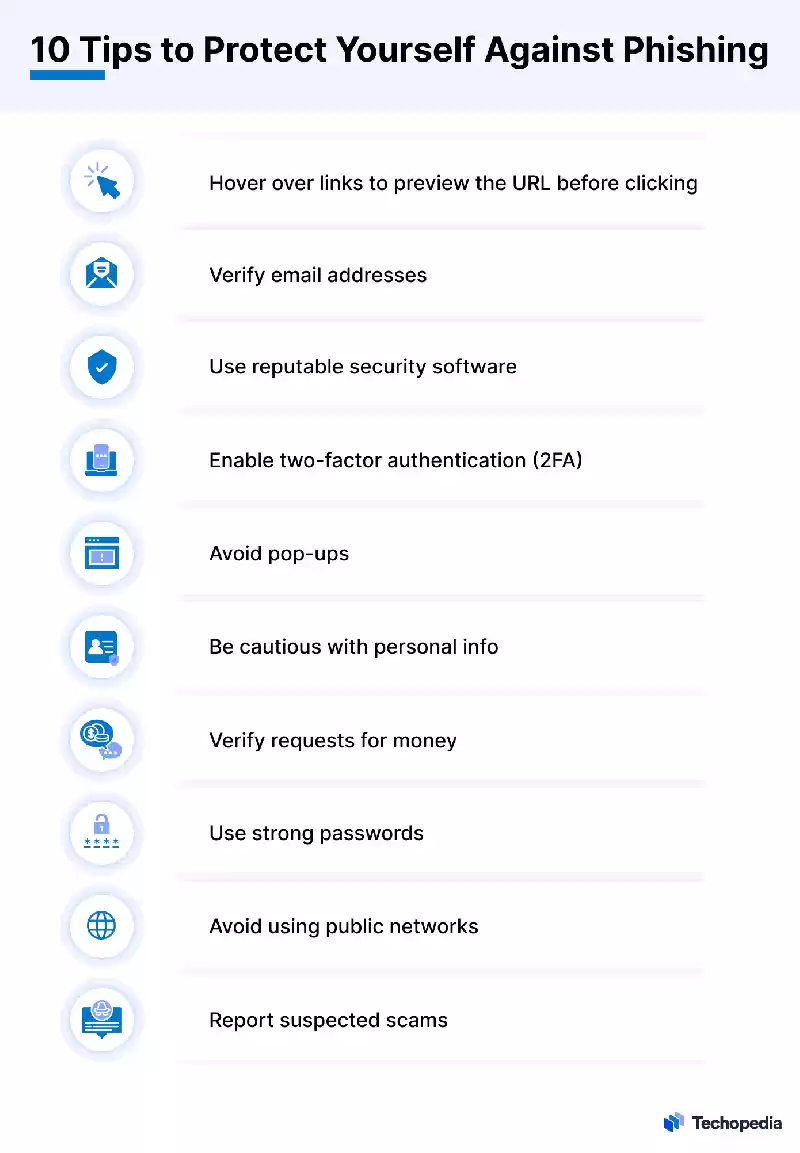
The following protection precautions are encouraged to save you phishing attacks from being a hit:
- Never open e mail attachments that aren't predicted;
- Never click on on email links that request personal statistics;
- Validate a URL earlier than clicking on it via hovering the Mouse Cursor over the link to display the real URL it ends in. The URLs have to in shape;
- Never click on hyperlinks that start with HTTP in preference to HTTPS;
- Be suspicious of all telephone calls requesting individually identifiable data (PII) or the transfers of budget from one account to some other;
- Don’t answer cell cellphone calls from unknown numbers;
- If a person calls claiming to be from a central authority company or a legitimate business enterprise, dangle up and make contact with the wide variety at the legitimate internet site of that company or organisation;
- Never deliver out credit card numbers over the phone;
- Always allow UPDATEs for net browsers, running systems, and Software programs walking locally on net-on hand devices;
- Use updated pc security equipment, together with Anti-Virus Software program and subsequent-gen Firewalls;
- Verify a website’s cellphone wide variety before putting any calls to the Smartphone quantity provided in an e-mail;
- Use Strong Passwords and -thing Authentication (2FA) for all on line bills;
- Report suspected scams to the organisation the phisher is impersonating, as well as authorities authorities including the Federal Trade Commission (FTC);
- If relevant, have the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) team review and decrease the range of corporate debts with get admission to to vital records and devices, restriction password sharing, and reduce opportunities for Privilege eScalation by proscribing access privileges.
Anti-Phishing Software
Anti-phishing software program can be thought of as a cybersecurity toolkit that employs a extensive variety of techniques to discover and neutralize phishing threats. Here are some key capabilities and capabilities of anti-phishing software program suites:
- Email Filtering: Anti-phishing solutions often encompass e-mail filtering abilities to experiment incoming messages for suspicious content material and analyze sender addresses, email content material, and embedded links to perceive phishing tries. Adaptive e mail protection apps can stumble on extraordinary behavior and robotically limit an employee’s get admission to to sensitive facts and systems.
- Link Analysis: These equipment look into URLs within emails or messages to affirm their legitiMacy. They compare the hyperlinks against known Blacklists of malicious domains and determine their popularity.
- Content Analysis: This type of anti-phishing software program analyzes e-mail content, seeking out phishing signs which include misspellings, suspicious attachments, or requests for touchy information.
- Real-time Threat Intelligence: Many Anti-Phishing Services depend on Digital immune structures with real-time danger intelligence feeds to stay up to date on rising phishing threats and approaches. This helps in identifying and Blocking off new varieties of phishing campaigns directly.
- Machine Learning and AI: Advanced anti-phishing software employs ML and AI Algorithms to adapt and improve their detection abilities. They can recognize patterns indicative of phishing assaults, even in formerly unseen threats.
While anti-phishing software program and anti-phishing cloud offerings are bold guns against cybercriminals, it’s crucial to don't forget that human vigilance stays a crucial factor of powerful cybersecurity. No software can update the need for people to be cautious, skeptical, and nicely-informed about phishing threats.
Security focus training need to cross hand-in-hand with anti-phishing answers to create a strong protection posture.
Let's improve Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits) term definition knowledge
If you have a better way to define the term "Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits)" or any additional information that could enhance this page, please share your thoughts with us.
We're always looking to improve and update our content. Your insights could help us provide a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits).
Whether it's definition, Functional context or any other relevant details, your contribution would be greatly appreciated.
Thank you for helping us make this page better!
Here is a list of the most searched for the word Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits) all over the internet:
- Phishing attack examples
- Spear phishing
- Who are the targets of whaling phishing attacks
- Types of phishing
- Is an indicator of pop-up phishing
- What is phishing
- Phishing attack website
- How to prevent phishing
Obviously, if you're interested in more information about Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits), search the above topics in your favorite search engine.
Frequently asked questions:
- What are the important questions about Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits) on the Internet?
- Some of the important questions related to Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits) are:
- Who are the targets of whaling phishing attacks
- Phishing attack examples
- How to prevent phishing
- What is phishing
- how do spear phishing attacks differ from standard phishing attacks?
- Types of phishing
- What is phishing in cyber security
- What is phishing in computer
- What is Phishing?
- Phishing is a protection Make the most in which a offender imPersonates a legitimate commercial enterprise or authentic Character in order to accumulate Private and sensitive Data inclusive of credit score card numbers, personal idEntity numbers (PINs), and Passwords.
Your Score to Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits) definition
Score: 5 out of 5 (1 voters)
Be the first to comment on the Phishing (Phishing Attacks; Phishing Exploits) definition article