ZTNA meaning
Last updated 25 month agoWhat is Zero Trust (ZTNA)?

What does ZTNA stand for?
Zero Trust (ZT) is a Records-centric Cybersecurity approach for company Computing that assumes no end-person, computing tool, net Carrier, or Network connection can be trusted — even when an get entry to request originates from within the enterprise’s own commUnity perimeter.
The Zero Trust version has advanced to bear in mind Distributed Computing and an ever-expanding Attack Surface. Unlike a unmarried sign-on (SSO) approach that allows customers to log in as soon as and get right of entry to a couple of network services without re-entering Authentication factors, Zero Trust requires authentication elements to be confirmed — and re-proven — whenever a commuNity useful resource is asked.
Because untrusted risk actors exist each Internally and external to a network, Zero Trust supports the subsequent ideas:
- Never Trust
- Always Verify
- Enforce Least Privilege
An vital aim of the Zero Trust Model is to prEvent malicious actors from the use of a compromised account to transport laterally across a target network.
What Does Zero Trust Mean?
In the past, cybersecurity efforts have been focused on shielding the network perimeter. With the increase of the dispensed Cloud and area computing, network factors that traditionally weren’t part of get entry to manage decisions have turn out to be crucial — and want to be covered just like every other assault surface.
How Zero Trust works
Zero Trust protects vital records and resources each outside and inside the conventional network perimeter by means of the use of records accrued in actual-time from more than one sources. This requires DevOps teams and safety Engineers to work collectively and layout an incorporated set of safety processes capable of inspecting and logging all sorts of network site visitors.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) uses the Principle of Least Privilege (POLP) to limit access to network resources. ZT Identity and Access Management (IAM) approaches rely on a combination of Contextual factors, such as Username, Password, Device kind, IP deal with, and physical vicinity to determine whether an access request need to be allowed or denied.
Microsegmentation is gambling an important position in Zero Trust as it logically breaks a large network into smaller, extra potential segments. Dividing the community into microsegments permits community security engineers to Discover and comprise intrusions appreciably faster and extra efficiently than is possible with traditional, monolithic cyberSecurity Architectures that are most effective designed to defend the community perimeter.
A Zero Trust architecture calls for a strong cybersecurity infrastructure able to making, logging, and enforcing get right of entry to choices for disparate (but related) cybersecurity competencies. Network and engineers will need to recognise the way to use Software Program-described Networking (SDN) and gadget learning (ML) Algorithms to search for inFormation styles that indicate malicious activity in real-time. To ensure get right of entry to control enforcement stays as granular as possible, protection engineers may even want to realize a way to work with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the robot Method Automation (RPA) Programming as a way to furnish or deny access permissions.
As IT groups transition closer to premier zero consider Implementations, there's an multiplied reliance on the usage of automatic tactics and structures to enforce security policies.
Zero Trust Challenges and Advantages
Zero Trust implementation isn't always easy. Moving to a Zero Trust security model calls for every body in an enterprise to apprehend and decide to the want for verification and re-verification requests.
At its first-Class, a a hit Zero Trust method will help Make certain harm may be quick contained and reMediated while a selected person credential, Hardware device, or community provider is compromised. When implemented poorly on the lower back cease, however, Zero Trust can motive Latency and a poor person revel in (UX).
Zero Trust vs. Risk-Based Authentication
A “chance-based totally authentication” scheme may be used to complement Zero Trust and decrease latency. Risk-based totally authentication allows safety engineers to rank the assets they need to shield primarily based on standards such as the hazard degree associated with a particular user’s IP cope with.
Instead of NEVER trusting and ALWAYS verifying, an RBA method can get rid of get admission to controls for interactions that deliver a low threat, however put in force Zero Trust for Transactions that pose a higher stage of chance. This hybrid model of Zero Trust will also be known as “Adaptive Authentication.”
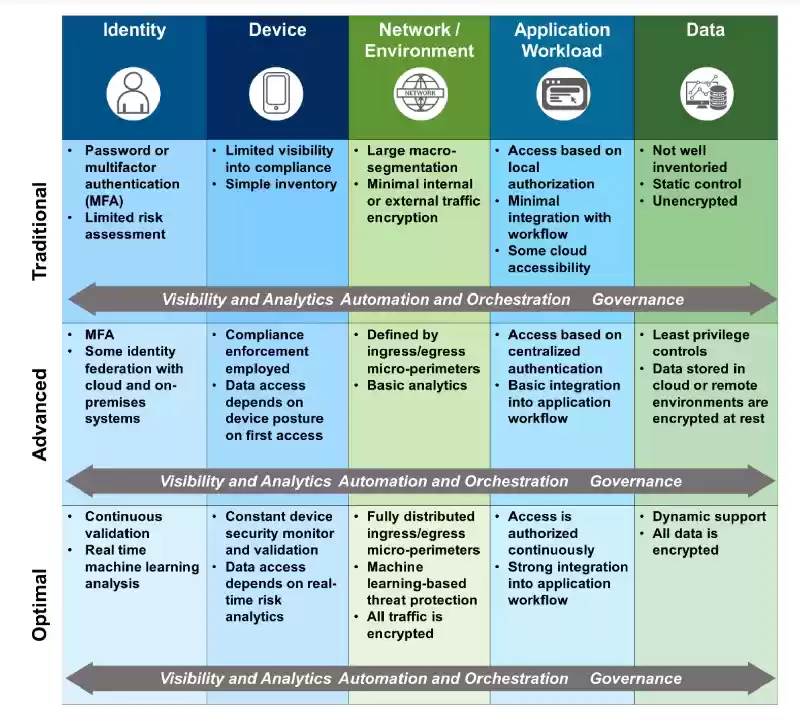
Zero Trust Maturity Model
The Zero Trust Maturity Model presents a Framework to assist agencies apprehend how close they're to absolutely implementing and optimizing a Zero Trust Architecture. A adulthood version is a sort of analytical tool that gives a framework for assessing how close a Business initiative is to assembly a favored set of middle ideas and requirements.
The Zero Trust Maturity Model may be used to assess progress towards 5 standards referred to as pillars:
IdEntity – How properly does a Zero Trust implementation use a mixture of factors to validate and Constantly verify an identification for the duration of the period of the identity’s interactions with offerings or facts?
Device – How powerful is a Zero Trust implementation with regards to assessing the Integrity of networked computing gadgets by using presenting security protections and visibility into the gadgets themselves?
Network – How intently does a Zero Trust implementation align community segmentation and protections with the needs of application workflows?
Application Workload – How correctly does a Zero Trust Architecture apply 0 agree with concepts to the development and Deployment of Software program applications via the use of non-stop integration and non-stop deployment to combine protection trying out and verification into every step of the improvement method?
Data – To what extent does the Zero Trust implementation use a facts-centric method to cybersecurity that requires IT staff to pick out, categorize and stock statistics assets as a way to prioritize Data Protection for his or her maximum important statistics property?
History of Zero Trust
While the term Zero Trust is frequently credited to John Kindervag, a few protection experts credit score Stephen Paul Marsh with coining the term.
A report posted via Forrester studies analyst, Dr. Chase Cunningham, entitled, “The Zero Trust eXtended (ZTX) EcosySTEM Report” delves further and descriptions how an eXtended Zero Trust framework can help networks, data, workloads, devices and people.
Your Score to Zero Trust article
Score: 5 out of 5 (1 voters)
Be the first to comment on the Zero Trust