MATIC meaning
Last updated 25 month agoWhat Is Polygon (MATIC)? Definition, Features, Pros&Cons, Future

What does MATIC stand for?
Polygon, previously known as Matic Network, is a Layer-2 Blockchain Protocol that runs parallel to the Ethereum bLockchain to supplement its operation. Launched in 2017, it brands itself as “Ethereum’s Internet of blockchains,” aiming to deal with troubles with scaling at the Ethereum blockchain via processing Transactions quickly.
Polygon is well matched with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and offers customers rapid transactions and near-0 processing (gasoline) expenses. As a Sidechain, Polygon is a separate blockchain from Ethereum, however wallet addresses are the equal on each blockchains.
Polygon can broaden custom blockchains, permit verbal excHange between Ethereum and different blockchains, and help other blockchains to become well suited with the Ethereum chain.
It operates a modified evidence-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism that allows validators to reach consensus with each block, not like conventional PoS mechanisms that require validators to sySTEM many blocks to attain consensus. Ethereum made the transition from proof-of-work (PoW) to PoS in 2022.
Users can Bridge their Cryptocurrency from different blockchains over to the Polygon network after which have interaction with applications that have been previously simplest reachable at the Ethereum blockchain.
The Polygon commUnity has tens of thousands of decentralized applications (dApps), Greater than three million common daily transactions, and $5 billion in secured assets, in line with its internet site.
History of Polygon
Here is a brief timeline of Polygon’s development:

Who Created Polygon?
Polygon became co-founded by using Jaynti Kanani, Sandeep Nailwal, Anurag Arjun, and Mihailo Bjelic, Software Engineers based in Mumbai.
What Is $MATIC?
MATIC is the Polygon blockchain’s local cryptocurrency coin. It is primarily based on Ethereum’s ERC-20 popular, so it is well matched with different Ethereum-based cryptocurrencies.
What Is $MATIC Coin Used For?
MATIC is used to pay transaction expenses at the Polygon commuNity. Holders also can stake their MATIC coins to secure the network in change for rewards and purchase Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) from marketplaces that run on Polygon.
MATIC coin is likewise used for governance, granting holders the right to vote on Modifications to the Polygon network’s improvement.
How Does Polygon Work?
Polygon runs as a parallel blockchain related to the principle Ethereum blockchain. It goals to supplement and improve Ethereum by using enforcing additional Functions for security, Modularity, and blockchain sovereignty to improve the person and Developer experience.
Polygon’s changed PoS consensus mechanism requires participants to stake their MATIC Tokens – meaning they agree to preserve them on the network and no longer trade or sell them – in trade for the right to validate community transactions and add them to the blockchain. Validators get hold of greater MATIC tokens as a praise for correctly validating each block. Delegators can stake their MATIC with out turning into a validator through oblique staking via a depended on validator.
Polygon’s mechanism is designed to Method transactions efficaciously whilst using the equal underlying technology as the principle Ethereum blockchain but with decrease costs. Contract addresses on the Polygon blockchain are different from Ethereum, and tokens must be bridged across the chains.
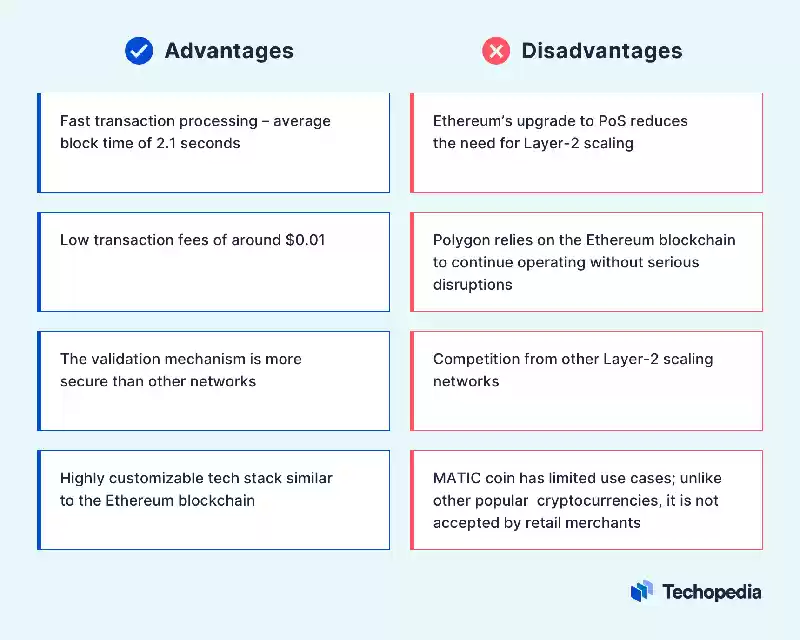
Pros and Cons of Polygon
Future of Polygon and $MATIC
The destiny of the Polygon network is tied to the main Ethereum blockchain, even though the Builders have emphasized that they purpose to ultimately amplify the protocol to different blockchains.
In 2021, Polygon StudiOS, launched as a subsidiary of Polygon Technology to consciousness on decentralized blockchain Gaming and NFTs.
The MATIC fee history reflects the Volatile nature of cryptocurrency markets, trading among a low of $ 0.003049 in May 2019 and an all-time excessive of $2.91 in December 2021.
The course of Polygon cryptocurrency’s destiny price will rely upon its use in transactions on the blockchain in addition to standard crypto market sentiment.
Your Score to Polygon (MATIC) article
Score: 5 out of 5 (1 voters)
Be the first to comment on the Polygon (MATIC)